Symptoms of prostatitis depend on the shape and causes of inflammation of the prostate gland and the presence of concomitant diseases. Symptoms are often crossed, which significantly complicates the diagnosis.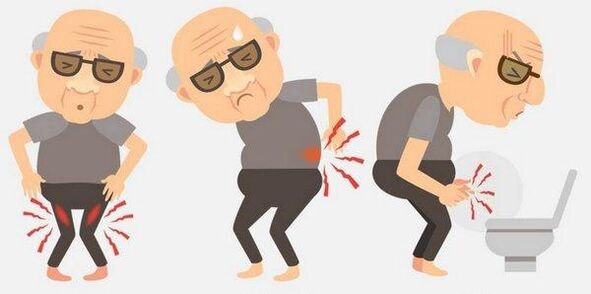
Chronic prostatitis
Chronic prostatitis develops as an independent disease or a complication of acute form of inflammation. During remission, the symptoms are weak or completely absent, and they become more shouted. The clinical picture resembles acute prostatitis.
The first symptoms of chronic inflammation:
- Frequent urgency of urination;
- Stupid pains in the lower abdomen;
- Discomfort in the prostate area (area to the testicles to the anus) in a long stay. Subsequently, it is impossible for burning to burn;
- Intermittent, painful urination;
- Boring pain in the rectum during emptying;
- The deterioration of the erection and the discomfort during ejaculation is possible.
In the chronic form of prostatitis, the above signals do not appear at the same time. Initially, it can be a lubrication orgasm, premature ejaculation, then a person should filter during urination, the pain is gradually connected.
In chronic inflammatory ultrasound, a decrease in prostate tissue density and the degree of reflection of the tissue wave. It is reduced in the presence of cysts or increases calcinates (stones), the focus of sclerosis (sealing from connective tissue, which is created due to acute inflammation). More and more in the late stages of connective tissue and fibrosis. The size of the prostate gland is reduced. During the visual diagnosis, it is difficult to distinguish it from the surrounding fiber.
Acute prostatitis
The acute form of infectious (bacterial) prostatitis is characterized by rapid development. The severity of the symptoms depends on the degree of damage to the gland. In the cataral form (inflammation only affects the channels), one can only feel a slight discomfort during the stress of the inguinal region. Iron is slightly increased and almost painless during the examination of iron.
Follicular (disturbed inflammation of the glands), parenhimal (inflammatory lesion of all tissues in the prostate) and abscesses (capsules with confusion) are manifested by a complete symptomatic complex:
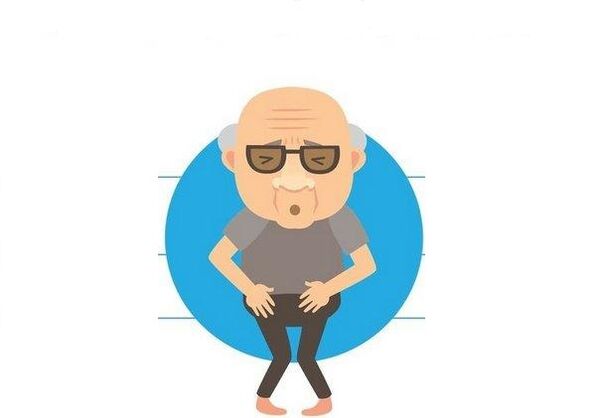

- Strong shooting in the groin, the rectum, the testicles, the sacrum, the inner hips of the hips, in the penis.
- Fever, general weakness. Active development of pathogens provokes body intoxication with inflammatory products.
- Transition during urination, feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder (due to irritation of sphincter and urethral mucosa).
- The purulent discharge from the urethra (PU -K is derived from the prostate channels and opens into the urethra).
- A feeling of severity in the perineum.
- Attack of a quick heartbeat.
- Wormy urine with turmoil. Blood may appear.
With the parenhimal shape of prostatitis, painful cramps and pulsating pain in the rectum, they make it difficult to empty. Little relief occurs only in a pose with pressed legs. The inflammation of the prostate often extends to the rectum and then the mucous membrane is extracted from the anus. The parenhimal form background urination may stop completely due to severe edema.
External signs of acute prostatitis with ultrasound:
- Expanding venous plexus. The vascular pattern can be expressed more clearly;
- Extension of the glandular channels and capsules (swelling, uneven growth, stinging outlines);
- The degree of increased reflection of the wave with the tissues;
- The seed bubbles on the prostate side are asymmetric due to the heterogeneous filling, and the seeds that remove the seed are expanded.
Suspicious tumors are prescribed MRI or CT.
Stagnant prostatitis
Stagnation of prostatitis (also called bacterial in the absence of infections) can occur in young and older men. The main symptoms are similar to infectious chronic inflammation. The distinctive feature is that discomfort from the urinary tract is manifested and increased, mainly due to long -term sexual abstinence. Aggravation can cause violent extension of sexual intercourse, a non -core orgasm (without inadequate emotional coloring). Far, painful urine (migration) is usually observed in the morning. However, if the previous day was a complete orgasm, there are no cramps.
This type of prostatitis In the secret of the gland, the amount of leukocytes does not exceed the norm, and there is no pathogenic vegetation in the third part of the urine.
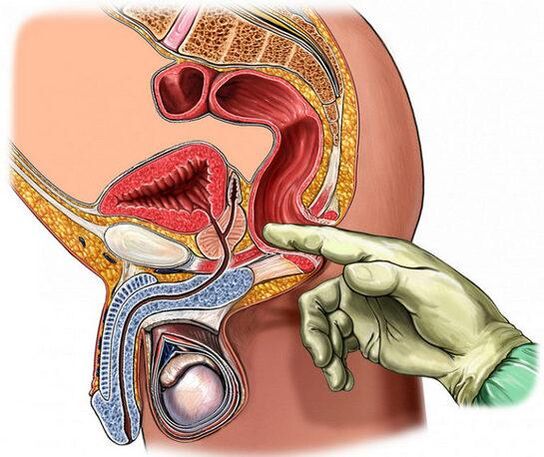
Calcular prostatitis
Calcular prostatitis has no specific symptoms. The presence of stones (calcinals) in the gland does not mean automatic inflammation. Physical effort can increase background pains. Migration of stones on wires sometimes provokes the appearance of blood in the urine.
Calcinates are detected during the ultrasound of the prostate. Due to increased density, the assets emitted more effectively.
Characteristics of prostatitis manifestation in a young and mature age
The symptoms of various forms of prostatitis do not depend on the age category. Young people are actively living in sexual life, so they develop more often in the acute form of infectious inflammation, with the right pronounced signals.
Chronic prostatitis is diagnosed in men a few years after sexual activity. During this time, due to the activity of hidden infections, the structure of the prostate is violated and the immunity of the cells is reduced. Symptoms occur at a time when abnormal changes are irreversible.
Mature men suffer primarily from urinary disorders, stupid pain and erectile dysfunction with perineum. Prostatitis at this age exacerbates stagnant processes of the pelvis against the background of androgen failure and muscle tone loss.
When and to whom to contact
Any of the above symptoms are the cause of contact with the urologist or andrologist (diagnosis of prostatitis in clinical and home conditions). Many people avoid seeking a doctor because they have a negative attitude with their prostate finger through the anus or trusie (transrectal ultrasound). If the patient categorically rejects these types of examinations, the doctor offers a Transpabominal ultrasound - when the sensor bends against the lower abdomen. The bladder should be filled (only 350 ml of liquid one hour before the procedure).
Based on the results of ultrasound, the doctor determines the nature of the lesion of the tissue tissues and the bladder surrounding the lesion. To identify the cause of the inflammation, urine, blood, prostate secret (rectum massage), in some cases and a spermogram.
What diseases have similar symptoms
Many diseases have symptoms similar to prostatite. Above all, cystitis (inflammation of the bladder). This is characterized by frequent urging toilet, smeared in the lower abdomen, pain during urination, muddy urine, sometimes with blood. Perhaps a slight increase in temperature.
In men over 45, with the symptoms of prostatitis, the glandular and glandular cancer are primarily excluded. Inflammation against this abnormal background is often a secondary sign. The symptoms of glandular cancer are similar to manifestations of chronic forms of prostatitis: periodic urinary disorders cause pain in the groin. The prostate is painless, finger testing, but there are dense nodes in its structure.
Distant night urination, urine -slow flow, feeling of incomplete emptying of bubbles, drip leakage from the urethra and difficulty of perineum are characterized by adenoma. The image is clarified with touch and ultrasound: the outlines of the prostate are retained, the consistency is elastic, the surface is smooth, and the iron is almost painless.
In the groin, urinary tract and pain can occur with non -infected stones of the prostate - calcinates are present, but there is no favorable environment for connecting to pathogens. In this case, the discomfort in this case triggers physical activity and ejaculation. With the feeling of prostate under the fingers, you can feel the chalk (crunch of stones), the body of the gland is dense, tuber, moderately painful.
Urine disorders characteristic of the chronic stage of the disease are also typical of sclerosis of the bladder sphincter (an obstacle to the urethra in the protruding form of the slaughter muscle). Pathology is often the result of prostate prostate. Men under the age of 40 are rarely diagnosed.
In the case of chronic prostatitis, they are often enlarged venous nodes (internal hemorrhoids). You can only find a special diagnostic tool. Symptoms:
- Pain in the anus, giving the sacrum and legs;
- Erection violations;
- Strengthening the pain of the rectum and perineum during the emptying or prolonged finding in a sitting position.
The contours and consistency of the prostate are unchanged. Secretly lack of abnormal changes.
In the area of the anus and perineum, pain occurs with proxy inflammation of the rectum. The characteristic feature is a strong burning sensation in the anus during and after emptying, given to the penis and legs. They urge frequent urination (every 20-30 minutes), followed by lacus in urine. Prscrekit often develops at the same time as prostatitis. In this case, parallel therapy for both diseases is required.
Symptoms of prostatitis are also manifested by tuberculosis of the gland. In the venture zone of a 20-40-year-old man. In the early stages of development, the disease is almost asymptomatic. Occasionally minor pains occur in the rectum and perineum. Breaking urination begins with the background of participation in the pathological process of the glands and communicates the urine channel.
Tuberculosis develops turmoil cavities in the body of the prostate. When they break through, the content flows into the urethra and gets out of the penis from the penis. Bacteria in the urethra irritate the mucous membrane and provide fast and painful urine. Through the grill, the PUs can spread into the rectum. In this case, the temperature, weakness, sweating, weight loss increases.
Conclusion
The prostate is closely linked through the nerve plexus to other pelvic organs, the inflammation of which gives symptoms similar to prostatitis. The doctor should distinguish (distinguish) prostatitis from other diseases and identifies the associated. The patient should not surprise the fact that in the case of symptoms of prostatitis, the examination is directed not only to iron but also to other organs, especially the rectum. It is important to exclude their involvement in the development of pain and urinary disorders, otherwise treatment will be ineffective.